SDI measurement (Silt Density Index)
Measurements of Silt Density Index (SDI) are carried out for relatively clean water supplies (water from waterworks) in order to determine the contents of colloids, thereby indicating how fast an NF or RO membrane will be clogged (fouling).
As colloidal materials vary considerably in form and character the measurements are only normative. The method is, however, considered the most applicable for predictions of the risks of fouling RO and NF membranes.
SDI calculation
Use the following procedure to calculate the SDI.
Insert the values measured for ti and tf:
ti = the time it takes to tap100 ml.
tf = the time it takes to tap100 ml after having filtered for 15 minutes.
T = the total test time (always 15 minutes)
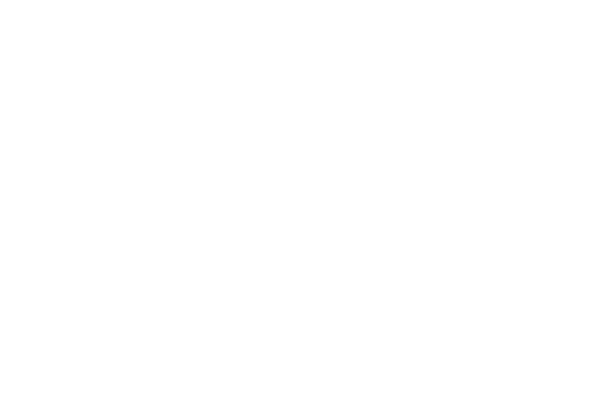
Video Guide
How to measure Silt Density Index
SDI measuring equipment
EUROWATER offers an SDI measuring equipment fitted with high quality components for an accurate SDI analysis.
For further information and request of data sheet, please contact your local sales and service office.
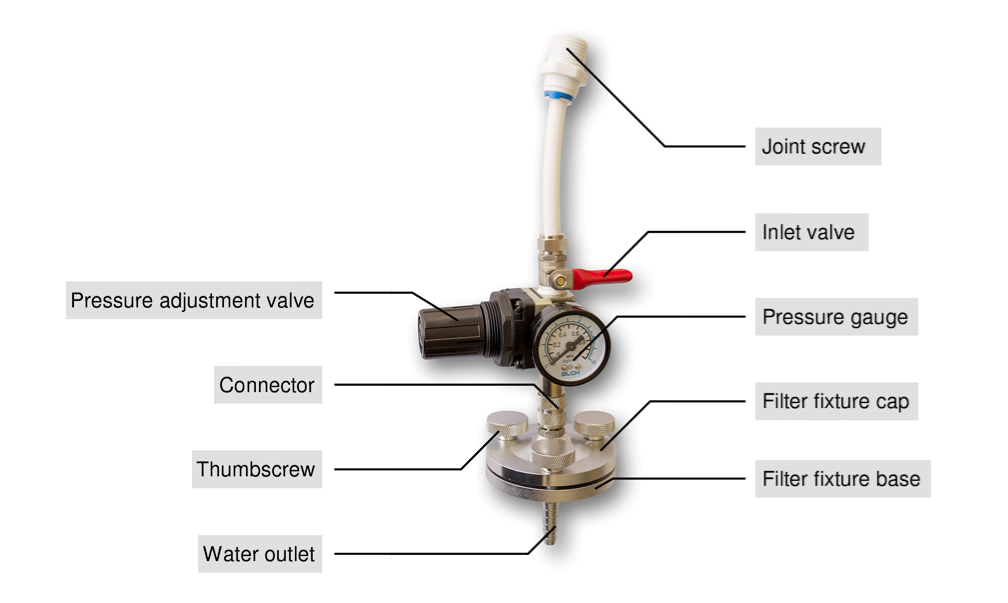
Reference sheet for calculated SDI
The sheet shows common measurements for quick reference. For reliable results, at least two measurements must have similar SDI values (+/- 0,5).
Example:
SDI1 = 3, SDI2 = 3,5: The measurement is acceptable
SDI1 = 3, SDI2 = 3,7: The measurement is NOT acceptable
SDI = 0-3: Standard conditions apply.
SDI = 3-5: Special operating data for recovery and permeate flow apply as stated in plant instructions.
SDI = 5-6: The water is not suitable for feeding an NF or RO plant unless the colloidal content is reduced by supplementary pre-treatment, i.e. flocculation.
Filters used for measuring
The filters show how colloids and suspended solids can foul the filter of the measuring equipment.
Water with an SDI >5 (right) is unsuitable for RO or NF treatment.

If your water is not suitable for RO and NF
Water with SDI above 5 is unsuitable for RO or NF treatment. But proper pre-treatment or alternative technologies can provide you with demineralized water.
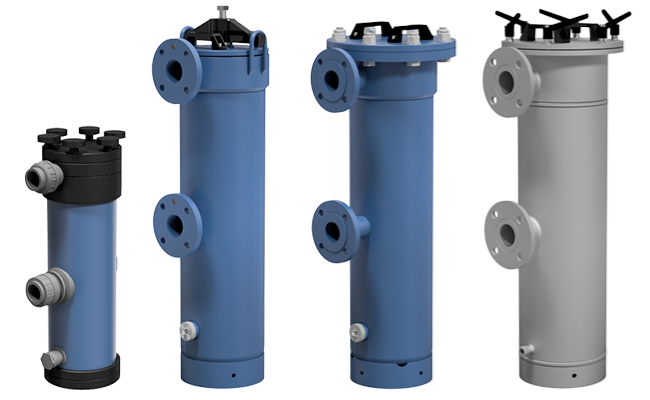
Bag filters
Pre-treatment is necessary to protect and extend the lifetime of the membranes. A bag filter has a robust design and comply with demands on flow rates and space.
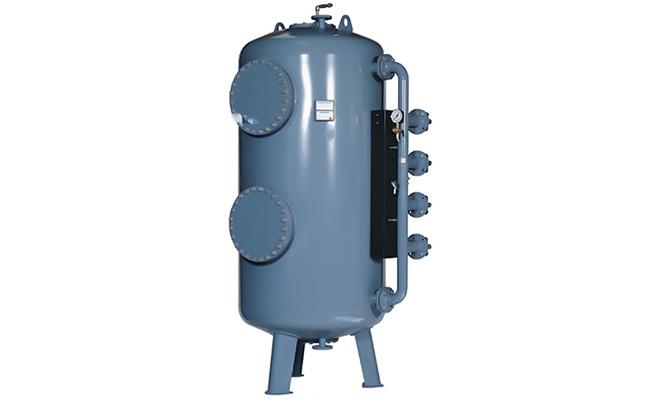
Pressure filter
A pressure filter can also function as a pre-filter to RO or NF. The content of metal and salts in the inlet water determine the selected filter material.
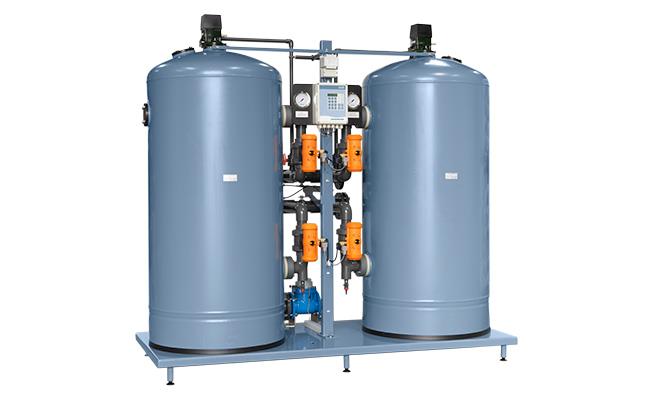
Softeners
Prevent hardness minerals from clogging the membranes by water softening. Softening can also be achieved through dosing of antiscalants that keep hardness minerals dissolved.
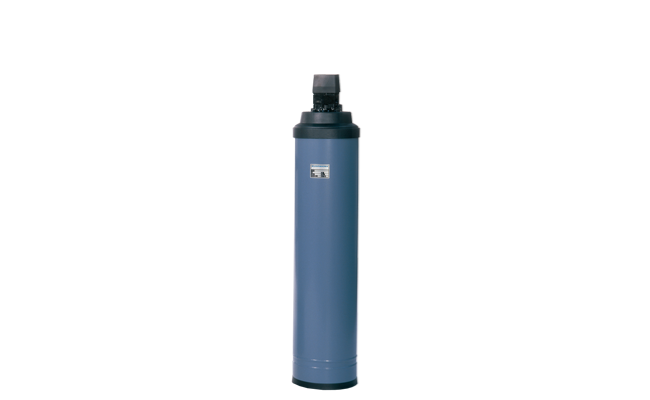
Activated carbon filter
A filter with a density of 1 µ protects the RO membranes against suspended solids. Free chlorine in the water can be removed in an activated carbon filter.
Demineralizer
A demineralizer requires no special pre-treatment of the inlet water to achieve demineralized water quality. The plant is very robust and use a two-column ion exchange system.

Contact us for further guidance
Our international sales and service organization is ready to guide you to an optimum solution based on your SDI value. Please contact us for further information.




